Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Drawing fancy boxes#
The following examples show how to plot boxes (FancyBboxPatch) with different
visual properties.
import inspect
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as mpatch
from matplotlib.patches import FancyBboxPatch
import matplotlib.transforms as mtransforms
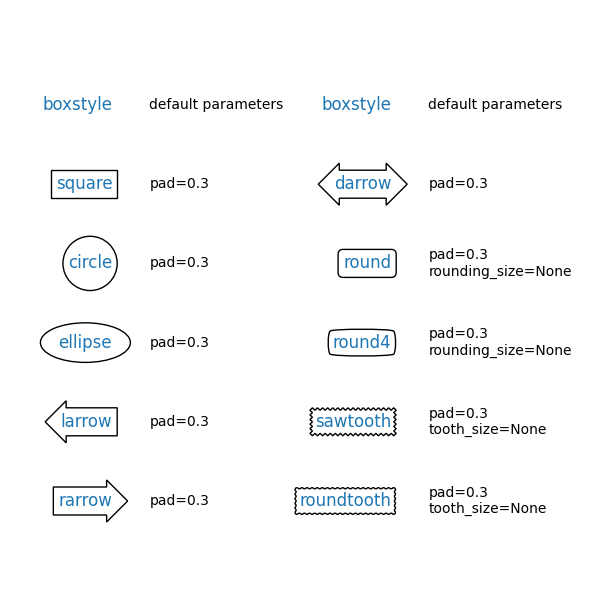
Box styles#
FancyBboxPatch supports different BoxStyles. Note that text
allows to draw a box around the text by adding the bbox parameter. Therefore,
you don't see explicit FancyBboxPatch and BoxStyle calls in the following
example.
styles = mpatch.BoxStyle.get_styles()
ncol = 2
nrow = (len(styles) + 1) // ncol
axs = (plt.figure(figsize=(3 * ncol, 1 + nrow))
.add_gridspec(1 + nrow, ncol, wspace=.5).subplots())
for ax in axs.flat:
ax.set_axis_off()
for ax in axs[0, :]:
ax.text(.2, .5, "boxstyle",
transform=ax.transAxes, size="large", color="tab:blue",
horizontalalignment="right", verticalalignment="center")
ax.text(.4, .5, "default parameters",
transform=ax.transAxes,
horizontalalignment="left", verticalalignment="center")
for ax, (stylename, stylecls) in zip(axs[1:, :].T.flat, styles.items()):
ax.text(.2, .5, stylename, bbox=dict(boxstyle=stylename, fc="w", ec="k"),
transform=ax.transAxes, size="large", color="tab:blue",
horizontalalignment="right", verticalalignment="center")
ax.text(.4, .5, str(inspect.signature(stylecls))[1:-1].replace(", ", "\n"),
transform=ax.transAxes,
horizontalalignment="left", verticalalignment="center")
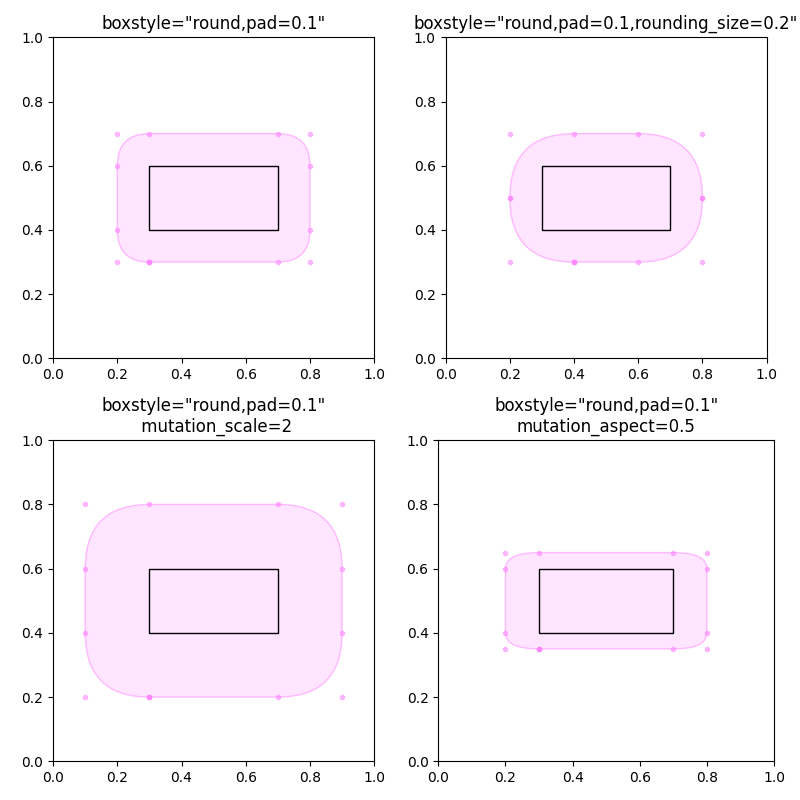
Parameters for modifying the box#
BoxStyles have additional parameters to configure their appearance.
For example, "round" boxes can have pad and rounding.
Additionally, the FancyBboxPatch parameters mutation_scale and
mutation_aspect scale the box appearance.
def add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, **kwargs):
kwargs = {
'facecolor': (1, 0.8, 1, 0.5),
'edgecolor': (1, 0.5, 1, 0.5),
**kwargs
}
fancy = FancyBboxPatch(bb.p0, bb.width, bb.height, **kwargs)
ax.add_patch(fancy)
return fancy
def draw_control_points_for_patches(ax):
for patch in ax.patches:
patch.axes.plot(*patch.get_path().vertices.T, ".",
c=patch.get_edgecolor())
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 8))
# Bbox object around which the fancy box will be drawn.
bb = mtransforms.Bbox([[0.3, 0.4], [0.7, 0.6]])
ax = axs[0, 0]
# a fancy box with round corners. pad=0.1
add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.1")
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1), aspect=1,
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.1"')
ax = axs[0, 1]
# bbox=round has two optional arguments: pad and rounding_size.
# They can be set during the initialization.
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.1")
# The boxstyle and its argument can be later modified with set_boxstyle().
# Note that the old attributes are simply forgotten even if the boxstyle name
# is same.
fancy.set_boxstyle("round,pad=0.1,rounding_size=0.2")
# or: fancy.set_boxstyle("round", pad=0.1, rounding_size=0.2)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1), aspect=1,
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.1,rounding_size=0.2"')
ax = axs[1, 0]
# mutation_scale determines the overall scale of the mutation, i.e. both pad
# and rounding_size is scaled according to this value.
add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.1", mutation_scale=2)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1), aspect=1,
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.1"\n mutation_scale=2')
ax = axs[1, 1]
# mutation_aspect scales the vertical influence of the parameters (technically,
# it scales the height of the box down by mutation_aspect, applies the box parameters
# and scales the result back up). In effect, the vertical pad is scaled to
# pad * mutation_aspect, e.g. mutation_aspect=0.5 halves the vertical pad.
add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.1", mutation_aspect=0.5)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1),
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.1"\nmutation_aspect=0.5')
for ax in axs.flat:
draw_control_points_for_patches(ax)
# Draw the original bbox (using boxstyle=square with pad=0).
add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="square,pad=0",
edgecolor="black", facecolor="none", zorder=10)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
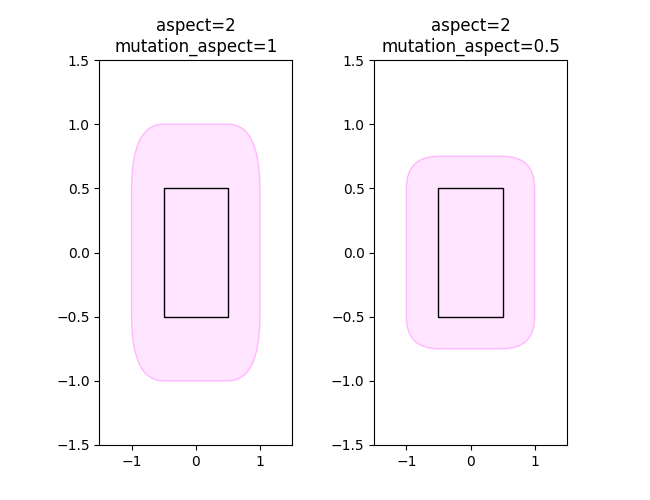
Creating visually constant padding on non-equal aspect Axes#
Since padding is in box coordinates, i.e. usually data coordinates, a given padding is rendered to different visual sizes if the Axes aspect is not 1. To get visually equal vertical and horizontal padding, set the mutation_aspect to the inverse of the Axes aspect. This scales the vertical padding appropriately.
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(6.5, 5))
# original boxes
bb = mtransforms.Bbox([[-0.5, -0.5], [0.5, 0.5]])
add_fancy_patch_around(ax1, bb, boxstyle="square,pad=0",
edgecolor="black", facecolor="none", zorder=10)
add_fancy_patch_around(ax2, bb, boxstyle="square,pad=0",
edgecolor="black", facecolor="none", zorder=10)
ax1.set(xlim=(-1.5, 1.5), ylim=(-1.5, 1.5), aspect=2)
ax2.set(xlim=(-1.5, 1.5), ylim=(-1.5, 1.5), aspect=2)
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(
ax1, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.5")
ax1.set_title("aspect=2\nmutation_aspect=1")
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(
ax2, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.5", mutation_aspect=0.5)
ax2.set_title("aspect=2\nmutation_aspect=0.5")
References
The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown in this example:
matplotlib.patches.BoxStyle.get_styles
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.241 seconds)